Deep Dive: Sanhua Intelligent (002050.SZ)
Stable cash cow + high-speed grower + large TAM new business; a quality company trading at 23x forward PE; Buy
Stable cash cow + high-speed grower + large TAM new business; a quality company trading at 23x forward PE; Buy
2025/01/03
Sanhua is regarded as a high-quality business in the A-share market. Initially, the company established itself in the air conditioning sector - not as a manufacturer like Midea or Gree, but as a key supplier of critical components, particularly valves, to major aircon makers, where it has secured a dominant market share. Leveraging its technical expertise from the aircon industry, the company successfully expanded into the automotive thermal management system (TMS) sector, and has become a significant player since entering Tesla’s supply chain in 2016. The expansion has fueled a new phase of growth for the company, especially with the rise of global EV penetration. In 2023, Sanhua further diversified by venturing into the humanoid robot industry through partnership with Tesla, potentially unlocking a third growth engine for the organization in the long term. Therefore, I see Sanhua’s business as a combination of a stable cash cow (aircon segment), a high-growth driver (auto segment), and a large-TAM new business (robot segment), each contributing to the company’s overall strength.
The company is currently trading at 23x forward PE, which is near the lower bound of its 5-year range. Considering its solid growth prospects over the next 5 years and the potential to be a long-term compounder, I feel the current market cap is underachieved. My DCF model indicates a 23% upside from the current price.
Investment thesis
Highly defensive aircon component business: The aircon valves market is highly defensive due to their high technical difficulties, criticality to aircon quality, wide variety of types, and relatively low unit price; Sanhua holds a dominant position in the global aircon valve market, with ~50% market share, particularly excelling in electronic expansion valves (EEV) and four-way valves. Sanhua’s segment revenue is expected to grow solidly for the next 5 years, driven by 1) increasing adoption of inverter aircons, 2) rising energy efficiency standards across countries (which boost valve demand), 3) growth in the commercial sector, and 4) government subsidies for equipment. With stable profitability, the segment will consistently generate positive cash flows for the firm
Increasing penetration of EV: Sanhua’s content value per EV is close to RMB 3,000, significantly higher than the RMB 100-200 per ICE vehicle; As EV adoption continues to rise globally (projected 16% Cagr in sales volume from 2023 to 2028 according to my model), Sanhua’s total addressable market is expanding
Increasing adoption of heat pumps in EV: Heat pumps are being increasingly adopted by car OEMs due to their superior energy efficiency, providing 20%+ battery savings in cold environments; as a leading provider of heat pump solutions, Sanhua stands to benefit from the trend, with OEMs expected to increase heat pump penetration by 20ppt within next five years according to my interview with industry experts
Increasing adoption of modules in EV: I am optimistic about Sanhua's push to supply more modules to OEMs, due to strong demand from the client side - modules make cars more lightweight, compact and efficient; enhance overall car assembly efficiency; simplify issue resolution; and streamline requirement specification. With module penetration expected to rise from 25% to 60%+ over the next five years, Sanhua has significant potential to boost its sales in the auto segment
Emerging opportunities in the newly entered humanoid robot industry: Sanhua is actively working with Tesla to supply actuators for its Optimus robots; while currently primarily a component integrator, Sanhua has potential to produce most key parts in-house or through partnership with other domestic firms, an effort that will enhance the price competitiveness of its solutions and greatly increase its share in the value chain. However, there are still considerable uncertainties regarding the viability and potential success of the humanoid robot industry, and I maintain a conservative forecast for the business line
Improving return metrics: Over the past five years, ROCE increased from 19.1% in 2018 to 28.2% in 2023, ROIC from 15.5% to 21.5%, and ROE from 15.2% to 18.7%; rising returns reflect that recent investments, particularly in the auto sector, are yielding strong returns, and an overall improvement in the company's operational efficiency, a testimony of management’s capabilities
Fair valuation with good upside: The company is trading at 23x 2024 earnings, which is near the lower end of its five-year range; I believe the market may be overly pessimistic about the company's growth prospects, and my DCF analysis indicates a 23% upside from the current price
Company history
The company was founded 40 years ago in 1984 in Zhejiang province, China. In its early years, it mainly produced products such as solenoid valves (for refrigerator), three-way valves (for aircons), and thermal expansion valves (for cars). In 1994, Sanhua formed a joint venture with Japan’s Fujikoji, which marked the former’s formal expansion in the aircon component market, leading to the development of additional aircon products like four-way valves, shut-off valves, and electronic expansion valves (EEVs).
In 2005, Sanhua Intelligent went public in Shenzhen Stock Exchange. Following the IPO, Sanhua pursued a series of acquisitions to broaden its capabilities and global presence. In 2007, the company acquired the global four-way valve business from Ranco Group (U.S.); by 2008, four-way valves accounted for nearly 50% of the company’s revenue, while shut-off valves, which contributed ~60% of revenue in previous years, represented 20% of total revenue. In 2012, Sanhua expanded into the home appliance market by acquiring Aweco (Germany), which produces key components for dishwashers, washing machines, and coffee machines. In 2015, Sanhua acquired 100% equity of Sanhua Microchannel, and later in 2017, acquired Sanhua Automotive to accelerate growth in the automotive sector with products such as EEVs, thermal expansion valves, water pumps, oil pumps, chillers, and cooling plates.
Since 2023, Sanhua has ventured into the humanoid robotics space in collaboration with Tesla, developing expertise in actuator manufacturing. This initiative has the potential to create a new growth driver for the company in the medium to long term.
Air conditioner components (60% of revenue in 2023)
The products: Sanhua produces various types of valves (including EEV, four-way valves, shut-off valves, globe valves, and solenoid valves) and microchannel heat exchangers for aircon manufacturers, as well as heating systems for dishwashers and coffee machines. Valves are critical components that control the speed, volume, direction, and pressure of the liquid refrigerant within the cooling/ heating system, and are essential for air conditioners to achieve high energy efficiency. Sanhua supplies both domestic (Media, Gree, Haier, Aux…) and international (Carrier, Trane, York, Panasonic, Daikin, Mitsubishi, Toshiba, Hitachi…) aircon makers, catering to both residential and commercial segments
The valves market is highly defensive: 1) valves are technically complex, requiring significant R&D investments to reach high-level of product quality, along with substantial capex to achieve economies of scale and competitive pricing; 2) valves are essential for aircon’s energy efficiency but are relatively inexpensive individually and come in various types - making it economically unworthy for aircon manufacturers to produce them in-house. This market structure protects vendors like Sanhua from competition from their big-sized clients and creates high barriers for new entrants. As a result, the valves market is stable and highly consolidated, with leading firms continuing to gain shares - CR3 is above 95% for key product types like EEVs and four-way valves.
Sanhua’s dominant position in the valves market: Sanhua has 50%+ market share in both EEVs and four-way valves, the two most critical valves for air conditioners, consistently ranking global number one for multiple years. Sanhua has set itself apart with superior product quality that provides more reliable performance in application. One of Sanhua’s main competitors in the field is Dunan, also from China, but Dunan’s products are less reliable and 5-10% more expensive than Sanhua’s. In 2021, Gree made a significant investment in Dunan, becoming its largest shareholder (holding 38.5% stakes now). While this investment helped Dunan get more orders from Gree, it prompted other aircon brands to shift a portion of their previous Dunan orders to Sanhua. Overall, Dun’an’s segment revenue has declined from 65% of Sanhua’s in 2017 to 58% in 2023.
Continuous growth drivers for Sanhua: Despite the current high penetration of its products, Sanhua can still consistently grow its aircon business in the next few years due to following factors: 1) inverter aircons: the rising penetration of inverter aircons, driven by the demand for higher energy efficiency, will continue to boost the need for valves, particularly EEVs, where Sanhua holds 50%+ of the global market share; overall inverter penetration is around 60-70% now - already high in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, but still low in regions like Russia, India, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, presenting opportunities for increasing volumes in these markets and driving growth for Sanhua’s key product lines; 2) energy efficiency standards: stricter energy efficiency requirements for aircons both in China and internationally also drive further demand for valves - in China, the new energy policies in 2022 “downgraded” the previous Level 2 standard for aircons (out of 5 levels, with L1 being most energy efficient) to the new Level 3, which became the new entry standard, effectively raising entry bars; in Europe, adoption of heat pumps has been increasing due to higher energy efficiency requirements, and such regulations amplify the need for valves that ensure precise control of refrigerant flow within aircon systems; 3) equipment subsidies in China: the new government program offers consumers 15% subsidy (or 20% subsidy if buying equipment with Level-1 rating) off the sales price of new aircons if they opt to upgrade; the initiative could spur additional demand in the residential aircon market in China, which has been surpressed by sluggish new housing sales as of late; 4) commercial aircon: Sanhua’s current market share in the commercial aircon segment (which is comparable in total size to residential) - is not as high as in the residential segment due to its later entry; however, Sanhua’s products are gaining traction due to superior quality - according to company IR, they expect to increase market share in the commercial segment by MSD% over the next 3-4 years, and by mid-teens ppt in the longer term.
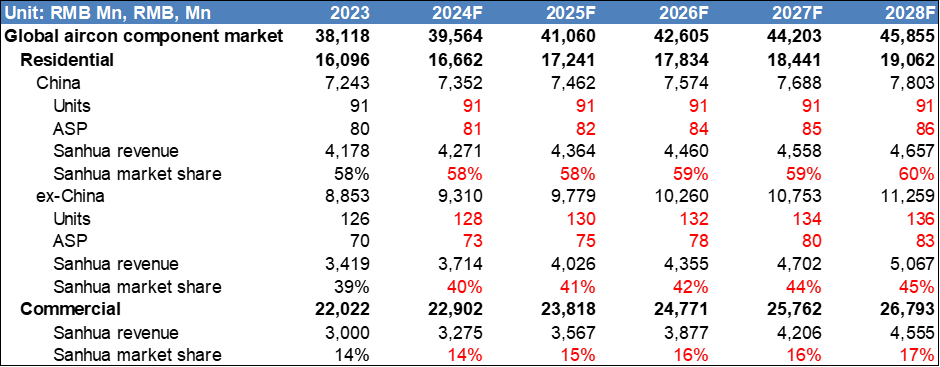
Putting all things together: I project the global residential aircon component market to grow by ~3% annually over the next 5 years, primarily driven by international markets, where ASP increases due to higher penetration of inverter aircons and stricter energy efficiency standards. I project Sanhua's market share of the global residential market to rise from 47% in 2023 to 50% by 2028, largely due to more advantageous product mix in the market (more EEVs), market consolidation, and increasing adoption of Sanhua’s products from overseas clients. For the commercial sector, I forecast a slightly higher market Cagr of 4%, with Sanhua gaining 3 ppt share from 2023 to 2028 - which is slightly lower than company expectations for conservativity - thanks to its current under-penetration in the segment. Net margins for the segment have been stable, averaging 11.1% over the past six years (2023: 11.1%), and I don't expect much changes going forward. Overall, I foresee the segment continuing to grow at Msd% over the next 5 years, with consistent margins and strong cash flow generation, contributing as a "cash cow" for the firm.
(Exhibit 1: Market sizing model of the aircon segment)
Automotive thermal management systems (40% of sales)
The products: Sanhua produces a variety of components for thermal management systems in both ICE vehicles and electric vehicles. Its product lineup includes valves (such as EEVs, thermal expansion valves, and solenoid valves), chillers, condensers, radiators, water and oil pumps, and cooling plates, while it currently does not produce other TMS components such as compressors, evaporators, pipes, sensors, tanks, and fans. In general, Sanhua tends to produce components that are of higher technical complexity (thus higher margins). Apart from individual components, Sanhua also supplies integrated modules by combining individual components to form sub-systems, helping clients achieve more efficient manufacturing.
Increasing penetration of EV: The total value of an EV's thermal management system can exceed Rmb 6,000, with Sanhua able to supply close to Rmb 3,000 worth of components. In comparison, a typical ICE vehicle's TMS is valued at around Rmb 2,000, with Sanhua contributing components worth Rmb 100-200. As EV penetration rises from 25% in 2023 to 50% by 2028, Sanhua's total addressable market is set to grow considerably.
Increasing penetration of heat pumps in EVs: EVs require either PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heaters or heat pumps for thermal management. PTC was once the mainstream choice due to its lower cost and simpler integration. However, heat pump systems are gaining traction because of their superior energy efficiency - according to tests by Autohome, EVs equipped with heat pumps consume 10-20% less battery power on average compared to those with PTC, with even greater energy savings in cold weather.
An expert from Ford shared that for larger EVs (which make up over 50% of Ford's vehicle lineup), ~70% of current production is already paired with heat pumps; the goal is to reach 90% penetration by the next platform generation (about 5 years per generation) and eventually approach nearly 100%. For smaller EVs, however, the penetration is just 10-20% now, and the expert did not anticipate a significant increase - smaller cars, with their limited space, may not benefit as much from the more expensive heat pump solution (on average costing Rmb 600 more than PTC) to justify the upgrade. Ford's level and speed of heat pump adoption is considered representative of the broader EV industry.
Sanhua is a clear beneficiary of the heat pump adoption trend. As a supplier that focuses exclusively on heat pumps (no PTC), the increasing adoption of heat pumps expands Sanhua’s revenue opportunities. Sanhua’s technical expertise in valves, which are critical to the performance of heat pump systems, also gives it a strong product edge in this area. Moreover, even if clients do not purchase complete heat pump systems directly from Sanhua, the company still benefits by supplying the multiple EEVs and solenoid valves (where it holds dominant market shares) essential to the heat pump systems.
Increasing penetration of modules: Sanhua is actively promoting the sales of modules - starting with small ones consisting of 2-3 individual components and scaling to larger ones that can be worth multiple thousand RMB. The good news is that, on the demand side, OEMs also have strong incentives to adopt more modules, especially in vehicles with higher MSRP, because modules: 1) make cars more lightweight, compact, and efficient through high levels of integration; 2) enhance overall car manufacturing efficiency by reducing assemble steps; 3) make issue resolution easier and quicker - instead of navigating layers of complex supply chain structures to resolve problems, OEMs can rely on a single point of contact (the module providers) to handle any problems within the module; 4) ease the requirement identification process by allowing OEMs to focus on overall performance requirements rather than specifying each individual component; and 5) enable some cost savings, as module vendors can achieve larger procurement volumes by combining orders from multiple OEMs; (having said that, OEM’s cost of purchasing modules, on balance, is still about 10% higher than assembling individual components due to margin given to module suppliers).
Given the benefits mentioned, the adoption of modules is on the rise. For example, in Ford’s vehicles, penetration of modules currently stands at 25% (with the remaining 75% procurement from individual components). Looking ahead, module penetration is expected to rise to 50% by 2026/27 and further to 60-70% by 2028/29, at which point most “suitable” vehicles will have transitioned to module solutions, with the remaining 30% being economy or low-priced cars that benefit more from the ~10% cost savings by sourcing and assembling TMS components in-house. Ford’s rate of module adoption is considered above industry average, with some peers (like Stellantis and Nissan) progressing more quickly, while others (like Toyota) are slower to adopt. The adoption of new modules, similar to heat pump penetration, also depends on platform changes, which typically occur every five years.
Sanhua is well-positioned to capitalize on the growing module trend. Selling modules allows Sanhua to increase its content value from clients. Additionally, Sanhua has a competitive edge due to its high rate of component self-production - according to company IR, 70%+ of the components within Sanhua-provided modules are produced in-house, a rate that is still increasing. This high level of self-production, coupled with high production efficiency, enables Sanhua to offer modules at more competitive price points - about 10% lower than international peers according to the Ford expert. In contrast, global Tier 1 like Denso, Valeo, and Mahle primarily produce only certain components, such as compressors, condensers, and evaporators in-house; when these companies supply a more complete module, they often need to source some key components like EEVs from Sanhua (or other vendors). A major domestic competitor, Toptech, which has 30% share of Tesla's TMS modules (with Sanhua holding the other 70%), also sources all valves from Sanhua, as instructed by Tesla, despite having the capability to produce some types of valves themselves.
Putting all things together: I forecast Sanhua’s automotive TMS business to grow at 35% Cagr through 2028, driven by two main aspects: 1) global EV penetration (incl. HEV/PHEV) to rise from 25% in 2023 to 50% by 2028, with China leading at 65% penetration by 2028, largely in line with industry forecasts; 2) TMS value per EV to increase by 3-4% Cagr due to increasing penetration of heat pumps; 3) Sanhua’s market share to grow from c.10% in 2023 to 17% by 2028, primarily due to its effort to successfully push for more module sales, which enhances its wallet share with major OEMs. Net margin of the segment was 13% in 2023, but I expect it to face higher pressure going forward as OEMs push for cost optimization; I forecast margins to decline to 11% by 2028, which is the current margin level of the aircon segment.
(Exhibit 2: Market sizing model of the auto segment)
Humanoid robots (0% revenue in 2023)
The products: Sanhua supplies actuator modules for Tesla's Optimus humanoid robots. Each Optimus robot comprises 28 actuators - 14 rotary and 14 linear - along with delicate hands, a battery pack, and FSD/AI chips. Within an actuator, key components are servo motor, speed reducer, encoder, and other mechanical parts - currently, Sanhua source most of these components from overseas suppliers, but the company is actively working on producing them in-house or collaborating with domestic partners.
Sanhua’s strengths: Sanhua got to work on this new endeavor with Tesla due to a unique combination of three things: 1) Sanhua possesses both mechanical and electronic expertise; 2) Sanhua has established large-scale manufacturing capabilities on key components, thanks to its hundreds-million-units capacity built in the auto segment; and 3) Sanhua has demonstrated strong R&D capabilities and responsive collaboration: it played a crucial role in developing Tesla’s three major iterations of TMS, including advancements like heat pumps, six-way valves, and eight-way valves; the quick adaptation and effective partnership have built trust between Sanhua and Tesla, leading to this new phase of collaboration in the humanoid robot sector. Sanhua is expected to capture around 70% of the actuator module share for Tesla's Optimus, similar to its share in Tesla's automotive TMS.
Opportunities for domestic substitutions: currently, most of the components Sanhua supplies in its actuator modules come from overseas manufacturers. This includes the harmonic speed reducer from Japan's HarmonicDrive Systems, the reverse planetary ball screw from Germany's Schaeffler, and encoders from an undisclosed foreign company. However, I believe there are big opportunities for Sanhua to produce most components in-house or through domestic partnerships. For instance, the company has successfully begun manufacturing servo motors internally, which were previously sourced from Japan's Kollmorgen, an achievement attributed to Sanhua's expertise from its auto business, where motor and speed reduction mechanisms are extensively researched. Sanhua has also established a JV with a leading harmonic speed reducer provider in China, to produce relevant components in Mexico for potential future deliveries. In the reverse planetary ball screw space, Sanhua is actively engaging with domestic firms like Beisite and Beituo to explore potential partnerships.
Domestic substitutions offer some key benefits to Sanhua: 1) increased value from the value chain: by producing components in-house or in collaboration with domestic partners, Sanhua can capture value from not only module integration, but also key components that make up the modules; 2) enhanced system understanding: involving in developing and producing components can enhance Sanhua's understanding of the system level integration; 3) cost reduction: domestic production in China offers significant cost reduction by tapping into the country's highly efficient manufacturing sector; this not only allows Sanhua to gain a cost advantage over its competitors, but is also essential for the humanoid robot industry to produce products affordable enough for mass adoption
Opportunities to expand beyond Tesla: Sanhua's revenue potential is not limited to Tesla, as other humanoid robot companies may also consider sourcing solutions from Sanhua. Currently, the core competencies and primary competitive focus of humanoid robot companies are centered on AI algorithms that control the robots' actions and interactions with humans - mechanical engineering is an area that many are willing to outsource. Additionally, many of these companies are still in development stages and face profitability challenges; producing mechanical parts in-house requires significant capex, which could quickly deplete their short-supplied cash reserves. Therefore, if Sanhua can advance its technology and production efficiency ahead of peers, it should have opportunities to supply other clients, and working closely with one of the leading players in the field (Tesla) should only help with its development speed and credibility. Having said that, Sanhua's IR team remains cautious, emphasizing their current focus solely on Tesla, which is understandable given their current stage of collaboration with the client. In my model, I did not factor in any potential revenue from other clients due to the uncertainties.
Big uncertainties in the viability of the humanoid robot industry: the current cost of production for a Tesla Optimus is nearly $100K, far too expensive for any meaningful level of adoption. Reducing the costs will depend on factors such as production scale and efficiency, domestic sourcing, and technological advancements. However, it is challenging to predict how much cost reduction can realistically be achieved at this stage. Tesla's long-term goal is to sell its robots for $20K each, at a scale of billions of units - still a very long way to go. Furthermore, the development of AI technologies integrated into these robots will also significantly influence their use cases and perceived value to customers. Therefore, there’re still a lot of uncertainties in terms of how large the humanoid robot industry will become, and I remain conservative in my model projections.
Financials
Top line: Revenue grow at ~17% Cagr in 2023-2028 driven by:
Aircon segment (60% of revenue): 6% Cagr in 2023-2028 mainly driven by: 1) increasing content value per aircon in overseas residential market due to increasing adoption of inverter aircons and stricter energy efficiency standards; 2) increasing market share of Sanhua (from 47% to 50%) in global residential segment; 3) increasing market share of Sanhua (+3 ppt) in global commercial segment due to current under-penetration
Auto segment (40% of revenue): 35% Cagr in 2023-2028 mainly driven by: 1) increasing global EV penetration from 25% in 2023 to 50% by 2028; 2) increasing TMS value per EV at 3-4% Cagr, due to higher penetration of heat pumps; and 3) increasing Sanhua market share in EV segment from c.10% in 2023 to 17% by 2028, due to its successful efforts to push for more module sales to clients
Humanoid robots segment (0% of revenue in 2023): grow to Rmb 10.9 billion by 2028, accounting for 15% of total revenue that year, driven by: 1) Tesla Optimus sales volume reaching 150K units in 2028, an forecast much more conservative than Tesla’s, with each actuator module sold (to Tesla) at Rmb 4.0K (or total USD 16K per robot); and 2) Sanhua capturing 65% share of Tesla’s actuator module supply (current industry forecasts at 70%)
Bottom line: Net income grow at 22.4% Cagr in 2023-2028 with NPM dropping from 11.9% to 10.9% due to:
Aircon segment: Maintain a stable net margin of 11% from 2023 to 2028, consistent with the average over the past six years (11%); this is a mature and consistent segment where margins have stabilized
Auto segment: Net margins to decline from 13% in 2023 to 11% by 2028 (aligning with the aircon segment), as the sector faces pricing pressure from car OEMs due to the latters’ ongoing cost optimization efforts
Humanoid robots: Net margins to rise to 10% by 2028 as the business scales; this margin will should be lower than the other segments’ as I believe the volume won’t reach optimal levels by 2028, and the market will still be in the growth phase
Return metrics: Over the past five years, ROCE increased from 19.1% in 2018 to 28.2% in 2023 (+9.1 ppt), ROIC increased from 15.5% to 21.5% (+6.0 ppt), and ROE increased from 15.2% to 18.7% (+3.5 ppt). Rising returns reflect that recent investments, particularly in the auto sector, are yielding strong returns for the business as the company strengthens its competitive edge in the market; it also reflects an overall improvement in the company's operational efficiency.
Capital allocations: from 2009 to 2023, the company allocated its generated cash flow in the following areas
70% on Capex: averaging around 10% of sales and even higher in recent years at 12.4% average over the past three years; with such capex investment, the company has been able to generate a net income Cagr of c.20% during the period
35% on dividend: reflecting a payout ratio of 40-50% or dividend yield 1-2% during 2020-2023
10% on other financial assets: mostly short-term investments
15% on addition to cash balance
-30% through debt raising to cover the deficit
Valuation: The company is currently trading at 23x 2024 earnings, nearing the lower bound of its five-year range. This is likely driven by concerns over slowing growth in the auto segment (which has been a key driver of the business's growth in recent years), and uncertainties surrounding the returns on investments in the humanoid robot sector - both of which have some merit. However, I feel the market can be overly pessimistic about the company's outlook - my DCF analysis indicates a target price of RMB 27.1, offering a 23% upside from the current price of RMB 22.0.
One thing to note is that this valuation assumes Sanhua’s humanoid robot business achieves some level of success, with an order volume of close to 100K units by 2028. While this target isn't overly ambitious, it still carries more uncertainties compared to the other two well-established segments in aircon and automotive. If we assume the humanoid robot industry fails and exclude that segment from the valuation, the potential upside decreases to 18%.
Pre-mortem
The downturn in the Chinese real estate market caused aircon manufacturers to reduce sales volumes in the domestic market, leading to significant order reductions for Sanhua and resulting in severe underutilization of its production capacities
Aircon manufacturers decided to produce valves in-house, aiming for long-term cost savings despite severe short-term margin impacts and considerable uncertainties regarding the long-term quality and reliability of their products
Stagnation in global EV industry growth caused Sanhua to lose growth momentum in its auto segment, which now accounts for 40% of the company’s total revenue
Advancements in auto TMS technologies rendered heat pump solutions obsolete, and Sanhua was not agile enough to adapt to new technology roadmaps
The humanoid robot industry turned out to be a fad, leading to the elimination of Sanhua's humanoid robot business line despite substantial investments in R&D and manufacturing capacities